Enhancing Biodiversity Through Agroforestry in Punjab
Introduction
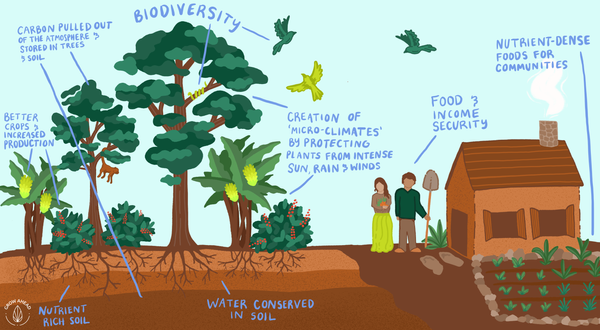
Punjab, a fertile region in northern India, is facing challenges of land degradation, soil erosion, and declining biodiversity. Agroforestry has emerged as a promising approach to address these issues while enhancing agricultural productivity and ecosystem services.
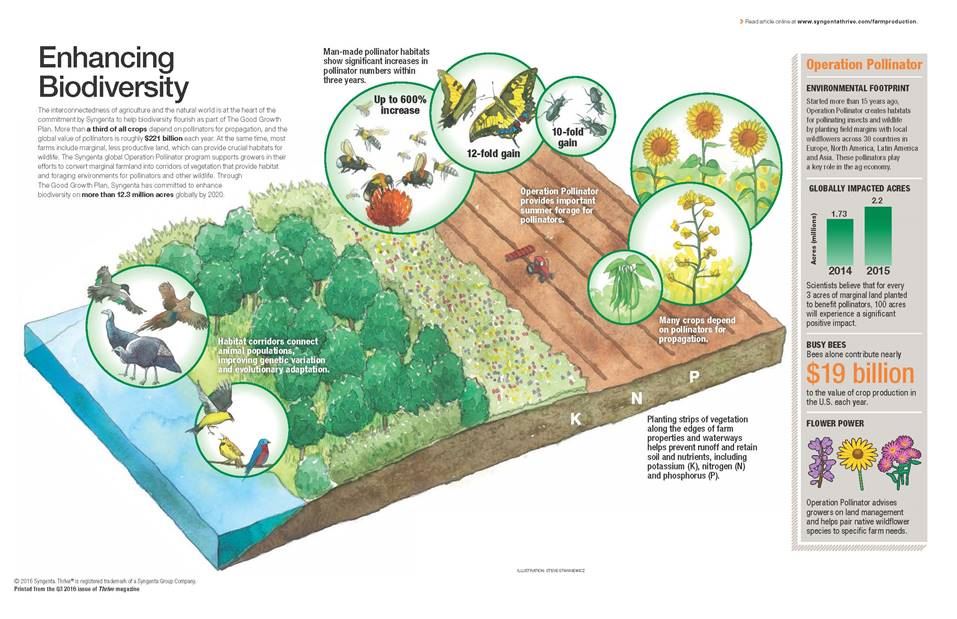
Agroforestry Practices in Punjab
Agroforestry involves integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural systems. In Punjab, common agroforestry practices include:
- Silvopasture: Integrating trees or shrubs into grazing lands for livestock.
- Alley cropping: Planting rows of trees or shrubs between crops.
- Windbreaks: Establishing rows of trees to shield crops from wind.
- Riparian buffers: Establishing trees along riverbanks to protect water quality and provide habitat for wildlife.
Benefits of Agroforestry for Biodiversity
Agroforestry practices provide numerous benefits for biodiversity:
- Habitat creation: Trees and shrubs create habitat for a wide range of species, including birds, insects, reptiles, and mammals.
- Increased structural diversity: Agroforestry systems introduce different vertical layers into the landscape, creating more complex and diverse habitats.
- Food and shelter: Trees and shrubs provide food and shelter for wildlife throughout the year.
- Pollination services: Flowers from trees and shrubs attract pollinators, which are essential for crop production.
- Erosion control: Trees and shrubs help prevent soil erosion, maintaining soil health and reducing sedimentation in waterways.
Case Studies
Numerous successful agroforestry projects have been implemented in Punjab:
- Silvopasture in the Kandi area: Integrating fodder trees and shrubs into grazing lands has improved livestock productivity, reduced soil erosion, and provided habitat for wildlife.
- Alley cropping in the Malwa region: Planting rows of Dalbergia sissoo trees between wheat crops has increased soil fertility, provided shade, and promoted biodiversity.
- Windbreaks in the Majha region: Establishing rows of Populus deltoides trees has protected crops from wind damage and provided habitat for birds.
Conclusion
Agroforestry is a valuable approach to enhance biodiversity, improve agricultural productivity, and address environmental challenges in Punjab. Through the implementation of agroforestry practices, the region can restore degraded land, reduce soil erosion, and create a more diverse and resilient ecosystem. The success of agroforestry in Punjab demonstrates its potential to promote sustainable agriculture and enhance environmental stewardship.## Enhancing Biodiversity Through Agroforestry In Punjab
Executive Summary
Agroforestry, an integrated approach that combines agriculture, forestry, and other natural resource management practices, presents a compelling solution to the challenges of biodiversity loss and environmental degradation in Punjab. By integrating trees, shrubs, and other perennial plants into agricultural systems, agroforestry offers a range of benefits, including enhanced biodiversity, improved soil health, increased carbon sequestration, and increased resilience to climate change. This article explores the potential of agroforestry to enrich the biodiversity of Punjab’s agricultural landscapes, examining its various components and benefits.
Introduction
Punjab, known for its fertile soils and agricultural productivity, is facing significant challenges in preserving biodiversity. Conventional farming practices, characterized by intensive monocultures and chemical inputs, have led to a decline in natural habitats, soil erosion, and a reduction in species diversity. Agroforestry offers a sustainable alternative, promoting biodiversity conservation alongside agricultural productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the key components of agroforestry systems?
A: Agroforestry systems typically include trees, shrubs, and perennial plants integrated with annual crops or livestock. The vertical structure created by these diverse species provides habitat for a range of wildlife.
Q: How does agroforestry benefit biodiversity?
A: Agroforestry creates diverse microhabitats that support a variety of flora and fauna. Trees provide nesting sites for birds, while shrubs offer cover for small mammals and reptiles. Additionally, flowering plants attract pollinators and other beneficial insects.
Q: What are the economic benefits of agroforestry?
A: Agroforestry systems can generate additional income streams from the sale of timber, fruits, and other products. The integration of trees can also enhance soil fertility, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and lowering production costs.
Subtopics
Tree Species Selection
Choosing the right tree species for agroforestry is crucial for ensuring biodiversity and productivity. Key considerations include:
- Native species: Opt for trees native to Punjab, as they are well-adapted to the local climate and support local wildlife.
- Multipurpose species: Select trees that provide multiple benefits, such as timber, fodder, fruits, and medicinal properties.
- Nitrogen-fixing species: Consider trees that fix nitrogen from the atmosphere, enhancing soil fertility and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Pollinator-friendly species: Choose trees that produce nectar and pollen to attract beneficial insects.
- Evergreen species: Incorporate evergreen trees to maintain biodiversity throughout the year.
Cropping Systems
The choice of crops grown in agroforestry systems influences biodiversity and overall productivity. Considerations include:
- Crop diversity: Cultivate a mix of annual crops to support diverse insect and bird populations.
- Crop rotation: Rotate crops to improve soil health and reduce pest and disease pressure.
- Cover crops: Plant cover crops during fallow periods to protect the soil, suppress weeds, and attract beneficial insects.
- Intercropping: Intercrop trees and other woody perennials with annual crops to create a more complex ecosystem.
- Organic farming practices: Implement organic farming techniques to promote biodiversity and reduce chemical inputs.
Livestock Integration
Integrating livestock into agroforestry systems can provide additional benefits for biodiversity and productivity:
- Grazing management: Controlled grazing can help maintain diverse plant communities and reduce fire risk.
- Manure application: Animal manure is a valuable fertilizer that can improve soil fertility and support soil biodiversity.
- Silvopasture: Combining forestry and grazing can create a sustainable system that provides timber, forage, and other products.
- Pollination: Livestock can help pollinate trees and other flowering plants, enhancing fruit and seed production.
- Habitat provision: Trees and shrubs provide shade, shelter, and nesting sites for livestock.
Soil Management
Healthy soil is essential for supporting biodiversity in agroforestry systems:
- Conservation tillage practices: Minimize soil disturbance to protect soil structure and organic matter.
- Organic matter management: Apply organic matter, such as compost and manure, to improve soil fertility and water retention.
- Mulching: Use organic materials as mulch to suppress weeds, retain moisture, and regulate soil temperature.
- Erosion control: Implement measures to control soil erosion, such as terraces, contour farming, and cover crops.
- Agroforestry buffers: Establish buffer strips of trees and shrubs along waterways to protect water quality and provide habitat.
Climate Change Resilience
Agroforestry systems can enhance resilience to climate change:
- Carbon sequestration: Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Water retention: Trees and shrubs help retain water in the soil, reducing runoff and flooding.
- Windbreaks: Trees and shrubs can act as windbreaks, reducing wind erosion and protecting crops.
- Heat tolerance: Agroforestry systems can provide shade and cool microclimates for livestock and crops.
- Adaptation capacity: Agroforestry systems can adapt to changing climate conditions by providing diverse habitats and supporting a variety of species.
Conclusion
Agroforestry offers a powerful approach to preserving biodiversity in Punjab while maintaining agricultural productivity. By integrating trees, shrubs, and perennial plants into agricultural systems, agroforestry creates diverse habitats that support a range of wildlife. The benefits of agroforestry extend beyond biodiversity conservation, including improved soil health, increased carbon sequestration, and enhanced resilience to climate change.
As Punjab faces the challenges of biodiversity loss and environmental degradation, agroforestry presents a sustainable solution that can enrich agricultural landscapes, support local communities, and safeguard the natural heritage of the region.
Keyword Tags
- Agroforestry
- Biodiversity
- Punjab
- Sustainable agriculture
- Climate change resilience